NFT Metadata: The Digital DNA Behind Your Digital Collectibles

NFT metadata is the underlying information that gives non-fungible tokens their unique characteristics, value, and functionality. While the NFT itself exists on the blockchain, the metadata contains all the descriptive elements that make each token special – from visual attributes to ownership history.
What Exactly Is NFT Metadata?
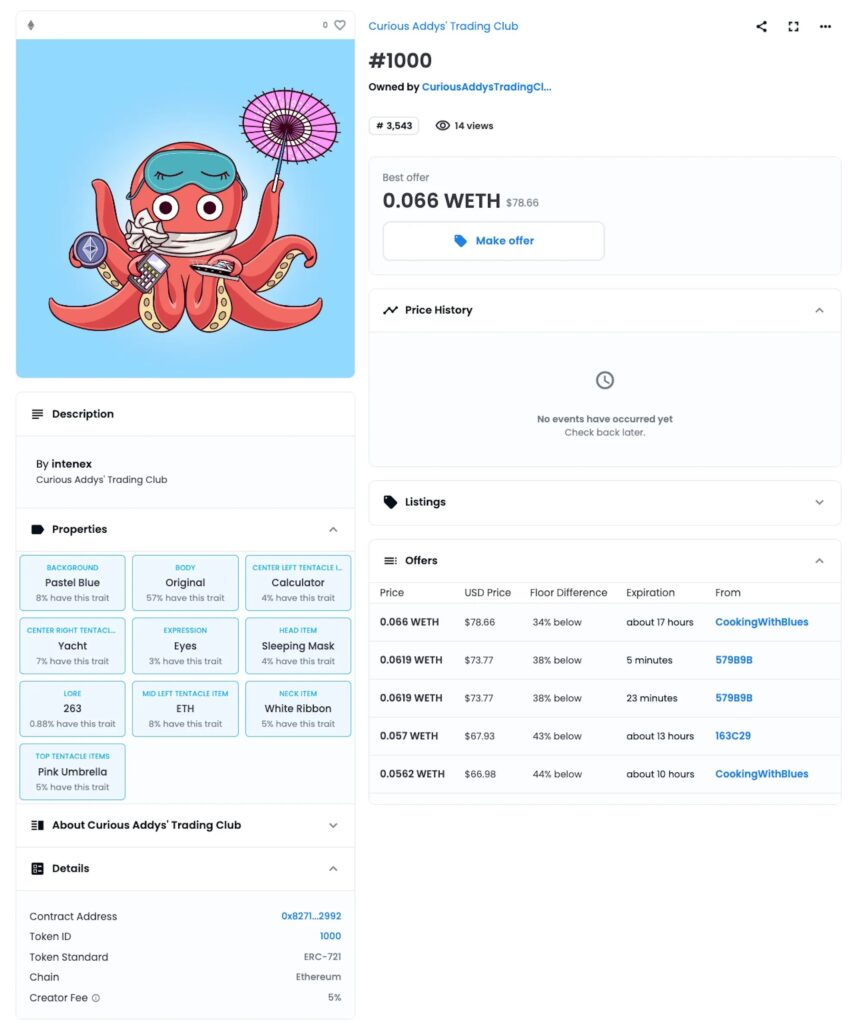
At its core, NFT metadata is structured information that describes and gives meaning to a non-fungible token. Think of it as the digital DNA that defines what your NFT actually represents. This metadata typically includes:
- Basic information about the digital asset
- Links to where associated media is stored
- Properties that define its characteristics
- Information about the creator
- Timestamp data
Without metadata, an NFT would simply be a meaningless token ID on the blockchain – the metadata brings it to life by connecting it to digital content and defining its attributes.
The Structure of NFT Metadata
NFT metadata is typically structured in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format, which provides a standardized way to organize information. Here’s what a basic NFT metadata structure looks like:
{
"name": "Cosmic Dreamscape #42",
"description": "A surreal digital painting depicting an otherworldly landscape",
"image": "ipfs://QmXoypizjW3WknFiJnKLwHCnL72vedxjQkDDP1mXWo6uco/42",
"external_url": "https://myartistwebsite.com/gallery/cosmic-dreamscape-42",
"attributes": [
{ "trait_type": "Background", "value": "Deep Space" },
{ "trait_type": "Style", "value": "Surrealism" },
{ "trait_type": "Color Palette", "value": "Cosmic" },
{ "trait_type": "Rarity", "value": "Uncommon", "display_type": "string" },
{ "trait_type": "Creation Date", "value": 1677721600, "display_type": "date" }
]
}
These key fields serve different purposes:
| Field | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Name | Identifies the specific NFT |
| Description | Provides context about what the NFT represents |
| Image | Links to the digital asset (art, video, etc.) |
| External URL | Points to additional information |
| Attributes | Defines specific traits that make the NFT unique |
Where NFT Metadata Is Stored
Where and how NFT metadata is stored has significant implications for the longevity and security of the digital asset. There are three primary approaches:
On-Chain Storage
With on-chain storage, the metadata is stored directly on the blockchain alongside the token itself.
Advantages:
- Complete decentralization
- Permanent and immutable storage
- Guaranteed availability as long as the blockchain exists
Disadvantages:
- Extremely expensive for large files
- Limited by blockchain storage capacity
- Not practical for media-rich NFTs
Off-Chain Centralized Storage
This approach stores metadata on traditional web servers or cloud storage solutions.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective for large files
- Familiar infrastructure for most developers
- Easy to update or modify
Disadvantages:
- Single point of failure risk
- Dependent on the hosting service continuing to operate
- Vulnerable to censorship or tampering
Off-Chain Decentralized Storage
This method uses decentralized storage solutions like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) or Arweave.
Advantages:
- Resistant to censorship
- More permanent than centralized solutions
- Content addressing prevents tampering
- More cost-effective than on-chain storage
Disadvantages:
- Still requires pinning services or incentive mechanisms
- Not as proven as traditional storage
- Can be slower to access than centralized alternatives
Metadata Standards and Protocols
Several metadata standards have emerged to ensure consistency across NFT ecosystems:
ERC-721 Metadata Standard
The original NFT standard for Ethereum introduced a basic metadata structure that includes name, description, and image URL.
ERC-1155 Metadata Standard
An extension that supports both fungible and non-fungible tokens with more sophisticated metadata options, including localization.
Metaplex Standard (Solana)
Used primarily in the Solana ecosystem, offering more extensive metadata capabilities designed specifically for NFT collections.
The Importance of NFT Metadata
Metadata plays several crucial roles in the NFT ecosystem:
Defining Value and Uniqueness
The attributes and properties in metadata often determine an NFT’s rarity and value. Collectors analyze these traits to assess uniqueness within collections.
Enabling Functionality
Smart contract functionality can be triggered based on metadata attributes, enabling NFTs to serve as access passes, game items, or other utility tokens.
Supporting Discoverability
Marketplaces and platforms use metadata to categorize and make NFTs searchable, helping collectors find assets that match their interests.
Preserving Provenance
Creator information and timestamp data in metadata help establish authenticity and ownership history, crucial for valuable digital collectibles.
Metadata Security and Permanence Challenges
The NFT space faces significant challenges related to metadata:
The Permanence Problem
Many NFTs point to metadata stored on centralized servers that could disappear, resulting in “broken” NFTs that no longer connect to their intended content.
Immutability vs. Flexibility
While blockchain immutability is valuable, it can create challenges when metadata needs to be updated or corrected.
Standardization Issues
Competing metadata standards and implementations can lead to compatibility problems across different platforms and marketplaces.
Emerging Trends in NFT Metadata
The NFT space continues to evolve with several emerging trends:
Dynamic NFTs
These tokens have metadata that can change based on external conditions or triggers, creating interactive experiences.
Rich Media Support
Metadata standards are expanding to better support complex media types like 3D models, interactive experiences, and layered content.
On-Chain Compression
New technologies are making it more feasible to store richer metadata directly on-chain through compression techniques.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Efforts are underway to create more universal metadata standards that work seamlessly across different blockchains and marketplaces.
FAQ: Common Questions About NFT Metadata
What happens if the server hosting my NFT’s metadata goes offline?
If your NFT’s metadata is stored on a centralized server that goes offline, your NFT may lose its connection to the actual content it represents. This is commonly called “link rot” and is one of the biggest risks in NFT ownership. To mitigate this risk, many projects are moving toward decentralized storage solutions like IPFS or Arweave, or implementing hybrid approaches that store critical metadata on-chain.
Can NFT metadata be changed after minting?
It depends on how the NFT was created. If the metadata is stored directly on-chain, it typically cannot be changed due to blockchain immutability. If the metadata points to an off-chain location, the content at that location could potentially be changed. Some NFT smart contracts are specifically designed with “mutable” metadata to allow for updates, evolutions, or dynamic content.
How do I check an NFT’s metadata before purchasing?
Most NFT marketplaces display the metadata associated with tokens, but for a more thorough inspection, you can:
- Find the token’s smart contract address and token ID
- Look up the token on a blockchain explorer
- Find the metadata URI in the token information
- Access that URI to view the raw metadata
Why are some NFTs more expensive when they look visually similar?
Visual appearance is just one aspect of an NFT’s value. The metadata often contains attributes that define rarity within a collection. Two visually similar NFTs might have very different rarity scores based on their metadata attributes. Additionally, factors like creator reputation, historical significance, and utility functions defined in metadata can significantly impact value.
How can I ensure my NFT’s metadata will be available in the future?
To maximize long-term availability:
- Choose projects that use decentralized storage solutions like IPFS or Arweave
- Look for NFTs that store critical metadata on-chain
- Consider using or supporting pinning services that maintain IPFS content
- Make personal backups of metadata and associated content when possible
- Support projects working on metadata permanence solutions in the blockchain space