Yield Farming in Crypto: The Complete Guide

Yield farming is one of crypto’s most powerful yet complex investment strategies. At its core, yield farming involves lending or staking your cryptocurrency assets to generate returns or rewards. Think of it as putting your crypto to work instead of letting it sit idle in your wallet. Farmers provide liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and receive rewards in return, often in the form of additional tokens or interest payments.
What Is Yield Farming and How Does It Work?
Yield farming operates on a simple principle: you provide your crypto assets to a platform that needs liquidity, and in return, you earn rewards. The process typically works through smart contracts on blockchain networks like Ethereum, Solana, or Binance Smart Chain.
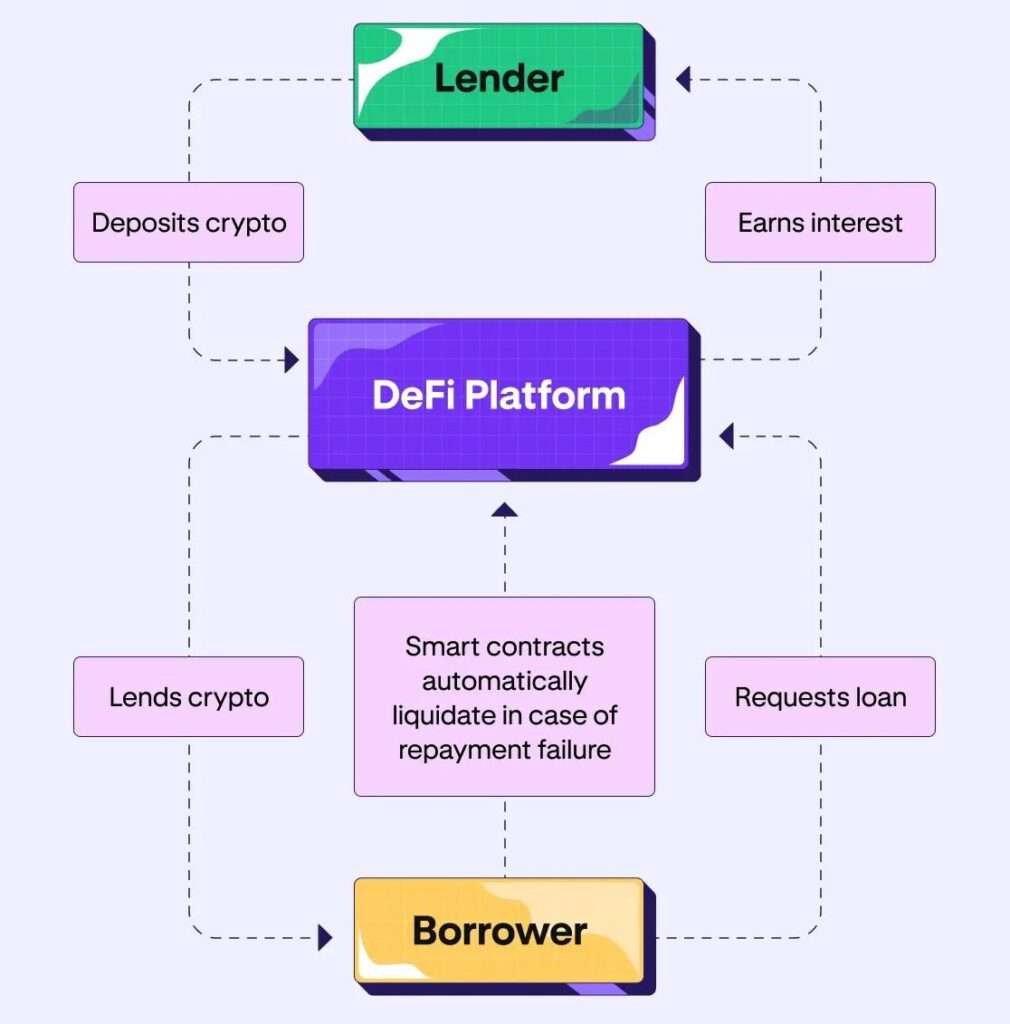
When you participate in yield farming, you’re essentially becoming a liquidity provider (LP). Your funds enter liquidity pools that power decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending protocols. These protocols need your assets to function smoothly, and they’re willing to pay for the privilege of using them.
The mechanics work in several ways:
- Liquidity provision: You deposit your tokens into a liquidity pool (often in pairs like ETH/USDC)
- Smart contract deployment: Your assets are managed by automated programs
- Fee collection: As other users trade or borrow against the pool, fees are generated
- Reward distribution: You receive a portion of these fees plus potential token rewards
Many yield farming opportunities involve providing liquidity pairs – equal values of two different tokens. When you deposit these pairs, you receive LP tokens representing your share of the pool, which you can later redeem for your original assets plus any earned rewards.
Types of Yield Farming Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Risk Level | Potential Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquidity Mining | Providing token pairs to DEXs | Medium | 5-20% APY + token rewards |
| Lending | Depositing assets in lending protocols | Low-Medium | 3-15% APY |
| Staking | Locking tokens to support network operations | Low | 4-12% APY |
| Yield Aggregators | Automated platforms that optimize yields | Medium-High | 10-100%+ APY |
| Leveraged Farming | Using borrowed funds to amplify returns | Very High | 20-1000%+ APY (with equivalent risk) |
Liquidity Mining
Liquidity mining involves providing token pairs to decentralized exchanges like Uniswap or SushiSwap. When traders swap tokens, they pay fees that are distributed to liquidity providers. Many protocols also distribute governance tokens as additional incentives.
For example, on Uniswap, you might deposit equal values of ETH and USDC. You earn a portion of the 0.3% trading fees from all trades that occur in that pool, proportional to your share of the total liquidity.
Lending Platforms
Lending platforms like Aave, Compound, and Maker allow you to deposit assets that others can borrow. In return, you earn interest on your deposits. These platforms typically pay you in their native governance tokens on top of the interest earned.
When you deposit assets on Compound, for instance, you receive cTokens (like cETH if you deposit ETH) that represent your stake plus accumulated interest.
Yield Aggregators
Yield aggregators like Yearn Finance automate the process of finding and switching between the highest-yielding opportunities. These protocols move your funds between different lending platforms and liquidity pools to maximize returns while minimizing the gas fees you would incur doing this manually.
Major Yield Farming Platforms
Several platforms have emerged as leaders in the yield farming space:
- Uniswap: The largest decentralized exchange with extensive liquidity pools
- Curve Finance: Specialized in stablecoin trading with lower slippage
- Aave: A leading lending protocol with multiple markets
- Compound: Another major lending platform with automated interest rates
- Yearn Finance: The original yield aggregator that automates farming strategies
- PancakeSwap: BSC’s largest DEX with farming opportunities
Each platform has its own token economics, risk profiles, and reward structures. The most successful yield farmers often use multiple platforms as part of their overall strategy.
Risks and Considerations
While yield farming can generate impressive returns, it comes with significant risks:
Smart Contract Risk
DeFi protocols rely on code that may contain vulnerabilities. Exploits and hacks have resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars in losses across the ecosystem. Before committing funds, research the protocol’s security audits and track record.
Impermanent Loss
When providing liquidity to trading pairs, price changes between the two assets can result in owning less total value than if you had simply held the tokens. This phenomenon, called impermanent loss, is a complex but critical concept for liquidity providers to understand.
If you provide ETH/USDC liquidity and ETH doubles in price, you’ll have less ETH (but more USDC) when you withdraw compared to if you had just held ETH. Your returns need to outpace this potential loss.
Market Risk
Crypto markets are highly volatile. Token prices, including reward tokens, can crash rapidly. Many farming tokens have limited utility beyond governance and can experience severe price drops when farming incentives decrease.
Gas Fees
On busy networks like Ethereum, transaction fees can significantly eat into profits, especially for smaller investors. Layer-2 solutions and alternative blockchains often offer lower fees but may have different risk profiles.
How to Start Yield Farming
If you’re interested in trying yield farming, here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Research thoroughly: Understand the platforms, their security history, and token economics
- Start small: Begin with established platforms and modest amounts
- Set up a wallet: Most farming requires a non-custodial wallet like MetaMask
- Acquire base assets: Purchase the tokens needed for your chosen strategy
- Connect to the protocol: Link your wallet to the platform’s interface
- Deposit funds: Follow the platform’s process to supply liquidity or lend assets
- Monitor regularly: Track your positions, rewards, and market conditions
- Consider tax implications: Yield farming transactions often create taxable events
For beginners, starting with lending on established platforms like Aave or providing liquidity on major DEXs like Uniswap is often recommended due to their relative simplicity and established security records.
The Future of Yield Farming
Yield farming continues to evolve rapidly. Several trends are shaping its future:
Cross-Chain Integration
As blockchain interoperability improves, yield farming strategies that span multiple networks are becoming more accessible. This allows farmers to access the best opportunities regardless of which blockchain they originate on.
Sustainable Tokenomics
Early yield farming protocols often suffered from inflationary token emissions that weren’t sustainable. Newer protocols focus on value accrual mechanisms that can maintain rewards over longer periods.
Risk Management Tools
The development of insurance protocols, risk scores, and automated portfolio management is making yield farming safer and more accessible to mainstream investors.
Institutional Adoption
As regulatory clarity improves, institutional investors are beginning to participate in yield farming through specialized funds and platforms, potentially bringing greater stability and liquidity.
FAQ: Common Yield Farming Questions
Is yield farming safe?
Yield farming carries significant risks including smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss, and market volatility. It’s safer with established protocols that have undergone multiple security audits, but no platform is entirely risk-free. Never invest more than you can afford to lose, and consider starting with smaller amounts until you understand the mechanics thoroughly.
How much can I earn through yield farming?
Returns vary dramatically based on strategy, platform, market conditions, and risk level. Conservative approaches like stablecoin lending might yield 3-10% annually, while more aggressive strategies can temporarily offer triple-digit returns (though these rarely last long-term). Higher returns almost always come with correspondingly higher risks. The DeFi space is constantly changing, so rates fluctuate daily.
Do I need a lot of money to start yield farming?
While you can technically start with any amount, gas fees on networks like Ethereum can make small-scale farming economically impractical. For smaller investments (under $5,000), consider farming on layer-2 solutions or alternative blockchains like Polygon, Avalanche, or Binance Smart Chain where fees are lower. Yield aggregators can also help make smaller positions more viable by sharing gas costs across many users.
What’s the difference between staking and yield farming?
Staking typically involves locking up a single token to support network operations (like in Proof-of-Stake blockchains) or to earn rewards from a protocol. Yield farming is broader and often more complex, involving strategies like providing liquidity pairs, moving assets between different protocols, or leveraging positions to maximize returns. Staking is generally considered lower risk than most yield farming activities.
How do taxes work for yield farming?
Tax treatment varies by jurisdiction, but in many countries, rewards from yield farming are treated as income at the time of receipt. Additionally, swapping tokens, adding/removing liquidity, and claiming rewards can all potentially trigger capital gains events. Keep detailed records of all transactions, as the complex nature of yield farming can create numerous taxable events. Consider consulting with a crypto-knowledgeable tax professional to ensure compliance.